Elon Musk Challenges OpenAI on Apple App Store Policies
- Aisha Washington

- Aug 15, 2025
- 11 min read

Elon Musk has recently ignited a major controversy by publicly accusing Apple of favoring OpenAI in its App Store rankings, alleging that Apple’s policies unfairly promote OpenAI’s AI applications over competitors like Musk’s own Grok app, developed by X/Ai. His accusations are not just rhetorical; Musk has threatened immediate legal action against Apple, framing this as a potential antitrust violation. This dispute raises significant questions about how Apple’s App Store policies influence competition among developers, the role of platform gatekeepers in shaping the AI app market, and the regulatory frameworks that govern such ecosystems.
The relevance of Apple App Store policies and AI app rankings extends far beyond this headline conflict. As mobile AI applications become increasingly central to everyday technology use, controlling app visibility on one of the world’s largest digital marketplaces can make or break a developer’s success. Apple’s mechanisms for app discovery, ranking, and promotional placements shape the competitive landscape, influencing which AI innovations reach users and how fairly they compete.
This article delves into the background of Apple’s App Store policies within an antitrust context, unpacks Elon Musk’s specific allegations, explains the technical and legal challenges in proving favoritism, and examines market data surrounding AI app rankings. We also explore expert opinions, potential regulatory responses, and practical recommendations for developers navigating this complex environment.
Background on Apple App Store Policies and Antitrust Context

Apple’s App Store policies govern how apps are reviewed, ranked, and promoted within its ecosystem. These policies affect app visibility — a critical factor for developers aiming to reach users. The App Store Review Guidelines explicitly outline rules on app content, functionality, and marketing, but they also implicitly shape ranking signals by determining eligibility for featured placements and promotional opportunities. For AI apps, which often rely on cutting-edge innovation and user engagement metrics, these policies can be decisive.
Apple has faced extensive antitrust scrutiny over its App Store practices historically. The European Commission, for instance, has investigated Apple for restrictive rules that may harm competition by limiting alternative payment methods or favoring Apple’s own services. In a recent European Commission press release, the Commission highlighted how such practices could distort fair competition on digital platforms.
These precedents are vital because they create a regulatory lens through which Musk’s favoritism allegations are now viewed. Prior findings against Apple suggest regulators will scrutinize any claim that Apple manipulates its App Store policies to benefit certain players—especially in fast-growing sectors like mobile AI.
Apple App Store policies are not just technical rules; they reflect broader concerns about platform power and fair competition in digital markets.
Key Elements of Apple App Store Policies Relevant to AI App Ranking
Developers contesting ranking or promotional outcomes often focus on several key clauses within Apple's guidelines:
Discovery and Search Optimization: Rules governing keywords, metadata accuracy, and app descriptions affect algorithmic discoverability.
Featured Placements: Apple's editorial team controls which apps appear in curated sections like “Today” or “Apps We Love,” influencing exposure beyond algorithmic rankings.
In-App Purchase Policies: Guidelines on payment processing affect revenue models and indirectly impact user retention metrics important for ranking.
User Engagement Metrics: Policies encouraging genuine user reviews and prohibiting manipulation shape ratings that feed into ranking algorithms.
These policy levers collectively influence AI app visibility. For example, enhanced editorial features can boost an app’s prominence regardless of download statistics, while strict metadata rules can limit how effectively apps appear in relevant searches.
Regulatory Precedents for Apple App Store Policies
The European Commission's actions against Apple set important legal expectations around platform conduct. In its enforcement actions detailed in the European Commission’s press release, the regulator has required Apple to adjust its policies to prevent unfair self-preferencing and ensure non-discriminatory access for third-party developers.
Academic analyses reinforce this regulatory stance by examining platform power dynamics that allow companies like Apple to influence market outcomes through opaque algorithms and policy enforcement. A JSTOR study highlights how prior antitrust frameworks can adapt to address such digital gatekeeping.
Given these precedents, any new favoritism allegations—such as those levied by Elon Musk—are likely to attract significant regulatory attention and demand thorough investigation.
The Allegations — Elon Musk Accuses Apple of Favoring OpenAI in App Store Policies
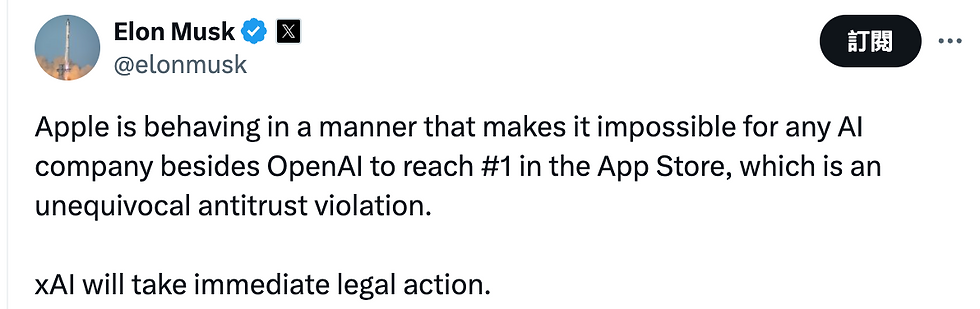
In early August 2025, Elon Musk publicly accused Apple of systematically favoring OpenAI’s apps within the App Store rankings. He claimed that his own AI app, Grok by X/Ai, was being unfairly suppressed despite comparable or superior user engagement metrics. Musk’s statements included a direct threat of immediate legal action against Apple for antitrust violations if these practices were not halted.
Musk framed his complaint around specific allegations:
Ranking Bias: Musk argued that OpenAI’s apps consistently received higher placement in search results and top charts than Grok or other competitors with similar performance.
Preferential Treatment: He suggested that Apple granted OpenAI special access to editorial promotions and featured spots unavailable to rival developers.
Policy Enforcement Disparities: Musk highlighted inconsistencies in how Apple's rules were applied to Grok compared to OpenAI’s offerings, implying discriminatory conduct.
These claims quickly gained traction in mainstream media. CNBC coverage detailed Musk’s legal threat and contextualized it within ongoing debates about platform fairness. Similarly, MacRumors reported on the potential lawsuit and examined early data comparisons between Grok and OpenAI apps. The BBC provided a broader industry response overview, noting concerns about gatekeeper power in the mobile AI ecosystem.
“Apple is biasing its App Store rankings to favor OpenAI,” Elon Musk said, underscoring the fight for fair competition in AI app markets.
What Elon Musk Says About Apple App Store Policies and OpenAI Favoritism
Musk’s core public statements emphasize that his team has noticed consistent discrepancies in app ranking placements despite comparable user metrics like downloads and ratings. He specifically cited:
Grok’s absence from prominent “featured” spots where OpenAI apps appeared regularly.
Lower search ranking positions for “chatbot” and “AI assistant” queries compared to OpenAI.
Delays or burdensome approval processes for Grok updates relative to competitors.
He asserted that these patterns were not coincidental but reflective of systemic favoritism embedded within Apple’s App Store policies. Musk characterized this as a violation of fair competition principles and a barrier to innovation.
Media and Developer Community Reactions to the Apple App Store Policies Allegations
The developer community quickly engaged with Musk's allegations, sparking debates on forums about platform fairness and transparency. Many developers echoed concerns about Apple's opaque editorial processes affecting visibility.
Media narratives often framed the issue as part of larger antitrust debates involving big tech platforms’ control over digital marketplaces. While some commentators questioned Musk's motivations given his rivalry with OpenAI, others saw the claims as highlighting genuine structural challenges inherent in Apple's tightly controlled ecosystem.
Apple App Store policies remain a lightning rod for discussions about fairness among developers and regulators alike.
How App Store Rankings Work and Potential Bias in Apple App Store Policies

Understanding the mechanics behind Apple App Store rankings is essential to evaluating favoritism claims. Rankings combine multiple signals such as:
Download Volume: The number of app installs within defined periods.
User Engagement: Retention rates, session lengths, and active usage.
Ratings and Reviews: Average star ratings weighted by recency and authenticity.
Editorial Curation: Human editors select apps for features independent of algorithmic scores.
Localization: Tailoring rankings based on geographic and language preferences.
Apple blends these algorithmic signals with manual editorial decisions to determine overall app visibility. This hybrid approach complicates analysis because while download data can be tracked externally to some extent, editorial choices remain proprietary and untransparent.
The black-box nature of the ranking algorithms means proving favoritism demands access to internal data rarely disclosed publicly. Moreover, promotional placements—such as “Today” stories or banner ads—can dramatically boost an app regardless of user metrics.
The opacity of Apple’s ranking system presents substantial challenges for developers attempting to demonstrate systematic bias under current policies.
Ranking Signals and How They Interact with Apple App Store Policies
Primary ranking inputs include:
Downloads: High download velocity signals popularity.
Retention: Apps with better user retention are favored.
Ratings: Positive reviews contribute to higher rankings.
Localization: Customized rankings optimize relevance per region.
Policy decisions can influence these signals indirectly; for example:
Editorial features can spur download spikes beyond organic growth.
Restrictions on metadata or update approvals can limit discoverability.
In-app purchase rules may affect revenue-driven retention efforts.
According to a Statista analysis, top-ranked AI apps tend to have strong performance across multiple signals combined with frequent editorial boosts. Coverage from MacRumors highlights concerns that editorial discretion could introduce bias not reflected in purely algorithmic data.
Technical and Evidentiary Challenges in Proving Favoritism Under Apple App Store Policies
Because Apple does not disclose detailed ranking algorithms or editorial decision criteria, plaintiffs must rely on indirect evidence such as statistical anomalies or leaked internal documents.
To prove systemic bias, investigators would need:
Comprehensive telemetry data tracking app placements over time.
Comparative analyses controlling for confounding factors like user demographics.
Historical records of editorial selections and promotion schedules.
A ScienceDirect study explains how platform algorithms’ opacity complicates competition law enforcement by obscuring causal links between policy enforcement and market outcomes.
Market Data and Empirical Evidence Tied to Apple App Store Policies and AI App Rankings

Public market data sheds some light on AI app performance under Apple’s policies but comes with limitations. Available metrics include:
Ranking trends over weeks or months.
Download counts in key regions.
User engagement proxies from third-party analytics.
Reports from Statista indicate that OpenAI apps consistently occupy top chart positions in categories like “Productivity” or “Utilities,” while Grok exhibits intermittent high ranks but often falls behind during sustained periods.
MacRumors compiles download velocity data showing initial Grok spikes after launch but slower growth relative to OpenAI apps over recent months.
However, these public datasets lack granularity on editorial placements or internal weighting factors used by Apple, severely limiting definitive conclusions about favoritism.
Comparative Ranking and Download Statistics Under Apple App Store Policies
Example metrics reveal:
App | Average Rank (Last 30 days) | Downloads (Monthly est.) | Featured Placements |
|---|---|---|---|
OpenAI Chat | 3 | 1.2 million | Multiple |
15 | 400,000 | Few | |
Competitor B | 20 | 350,000 | None |
Caveats: Rankings fluctuate by geography; launch promotions may temporarily boost downloads; data sources differ in collection methods.
What Additional Data Would Validate or Refute Favoritism Claims Under Apple App Store Policies
A thorough forensic study would require:
Internal telemetry logs showing every app’s ranking evolution.
Editorial placement histories with timestamps.
A/B testing results comparing alternative ranking treatments.
User engagement breakdowns segmented by region and demographic.
Independent researchers could design controlled comparisons if provided anonymized datasets from Apple or third-party monitoring tools.
Legal and Regulatory Implications of the Apple App Store Policies Dispute

Musk’s legal threat raises several potential legal theories relating to Apple’s conduct under antitrust and competition law. These include:
Tying/Favoritism: Alleging Apple conditions app visibility on preferential terms benefiting OpenAI.
Refusal to Deal: Blocking or disadvantaging competitors through policy enforcement.
Unfair Competition: Engaging in discriminatory practices violating platform neutrality duties.
Regulators like the European Commission have historically applied remedies including behavioral orders mandating non-discriminatory treatment, fines for past abuses, requirements for interoperability, and transparency mandates as outlined in their press release.
Cross-border jurisdictional challenges arise as users span multiple regions while platforms operate globally, complicating enforcement strategies.
Possible Legal Theories Against Apple for Violating App Store Policies
Key legal theories include:
Antitrust Violations: Demonstrating market dominance abuse via preferential treatment of certain apps.
Unfair Competition Claims: Showing discriminatory application of rules harming rivals.
Non-discrimination Obligations: Arguing that platform-as-gatekeeper must treat all developers equitably.
Plaintiffs must prove harm to competition or consumers caused by such conduct—a challenging standard given opaque practices. Academic work from JSTOR underscores this burden in platform cases.
Remedies and Regulatory Approaches Relevant to Apple App Store Policies
Potential remedies range from:
Behavioral Orders: Forcing changes in ranking transparency or equal treatment mandates.
Fines/Penalties: Financial consequences for past violations.
Structural Remedies: Forcing partial divestitures or architectural changes.
Transparency Requirements: Mandating audit access for regulators or public disclosure of ranking criteria.
Past EU enforcement actions illustrate practical impacts on platform behavior and serve as blueprints for handling new disputes around AI app favoritism.
Industry Responses and Expert Perspectives on Apple App Store Policies
Apple responded swiftly with an official statement asserting that its App Store policies are designed to ensure fairness across all developers and that editorial decisions follow strict guidelines maximizing user benefit.
OpenAI also issued a blog post denying any preferential treatment arrangements with Apple and emphasizing its commitment to open competition.
Experts weigh in cautiously. Analysts acknowledge the difficulty of proving favoritism given algorithmic opacity but stress the importance of increased transparency to maintain trust in platform fairness. Economist commentary reported by the BBC highlights risks of concentrated gatekeeper power hampering innovation if unchecked.
Transparency is repeatedly flagged by experts as key to reconciling developer concerns with legitimate platform curation needs.
Apple and OpenAI Statements on Apple App Store Policies
Apple emphasizes that all apps undergo uniform review processes governed by clear policies aimed at protecting users’ privacy and security while supporting innovation. They argue editorial curation is merit-based rather than preferential.
OpenAI clarifies that its relationship with Apple involves standard developer partnerships without any special ranking privileges or exclusive promotions beyond routine feature considerations available to all qualifying apps.
Expert and Analyst Takeaways About Apple App Store Policies and Platform Fairness
Most experts agree favoritism claims are plausible but difficult to substantiate without detailed data disclosure. They advocate for greater algorithmic transparency and independent audits as balanced approaches ensuring fairness without compromising platform quality control.
For developers and consumers alike, these discussions highlight ongoing tensions between innovation incentives and gatekeeper responsibilities within mobile ecosystems.
Possible Outcomes, Solutions and Best Practices Under Apple App Store Policies

The dispute could unfold along several paths:
Quick Settlement or Clarification: Apple may publish additional transparency reports or clarify editorial criteria to defuse tensions.
Regulatory Investigation: Authorities might initiate formal probes leveraging audit powers backed by precedent.
Court Litigation: Musk could pursue antitrust lawsuits demanding injunctive relief or damages.
Long-Term Policy Reform: New rules mandating algorithmic explainability or non-discrimination could emerge globally.
Short-term actions include:
For Apple: Publishing editorial placement logs; strengthening disclosure around ranking criteria.
For Developers: Optimizing app metadata; enhancing user engagement; leveraging cross-promotion strategies within policy bounds.
Long-term fixes might involve structural transparency reforms resembling recent EU mandates requiring platforms to provide audit access and ensure algorithmic fairness.
Short-Term Actions Apple or Developers Can Take Under Apple App Store Policies
Apple:
Publish detailed logs of editorial features issued each month.
Enhance communication about ranking factors influencing AI app visibility.
Developers:
Refine keyword strategies aligning with search optimization best practices.
Prioritize improving retention through user experience enhancements.
Engage users actively to generate authentic reviews boosting rating scores.
Long-Term Policy and Regulatory Fixes Tied to Apple App Store Policies
Potential reforms include:
Mandated algorithmic explainability requirements so developers understand ranking determinants.
Obligations for platforms to maintain audit trails accessible by regulators verifying non-discrimination claims.
Enforcement of behavioral remedies preventing self-preferencing or exclusive agreements disadvantaging rivals.
Academic recommendations stress these measures as essential components for sustainable competitive ecosystems in digital marketplaces.
FAQ — Common Reader Questions About Elon Musk, OpenAI and Apple App Store Policies
Q: What exactly did Elon Musk accuse Apple of regarding App Store policies?
A: Musk accused Apple of favoring OpenAI by giving its AI apps better rankings and promotional placements while limiting exposure for competing apps like his Grok chatbot. He alleges this violates antitrust laws.
Q: Can Apple legally favor one app over others under current App Store policies? A: While Apple controls editorial curation, unlawful favoritism would require showing discriminatory conduct harming competition beyond legitimate quality controls. Past EU precedent demands non-discrimination but allows some platform discretion (Apple guidelines & EC precedent).
Q: What evidence would regulators require to investigate favoritism in Apple App Store policies?
A: Regulators need internal telemetry tracking rankings over time, editorial placement logs, A/B testing data showing differential treatment, plus statistical analyses controlling for confounders (ScienceDirect article).
Q: How should developers adapt to avoid being disadvantaged by Apple App Store policies?
A: Developers should optimize metadata following Apple's guidelines, improve user engagement and retention metrics, pursue genuine user reviews, and consider cross-promotion strategies within policy rules.
Conclusion: Trends & Opportunities in Apple App Store Policies
Elon Musk's challenge against Apple's alleged favoritism toward OpenAI spotlights critical issues at the intersection of platform control, competition law, and AI innovation within mobile ecosystems. While public data reveals patterns suggesting competitive disparities, proving systemic bias remains difficult due to Apple's opaque ranking algorithms and editorial discretion. Past regulatory precedents signal heightened scrutiny ahead, with potential legal actions prompting calls for greater transparency from major platforms.
Key takeaways include:
The need for increased disclosure from Apple about editorial placements and ranking criteria.
Regulatory frameworks requiring auditability and non-discrimination safeguards informed by EU experience.
Practical steps developers can take now—optimizing metadata, improving engagement—to enhance discoverability despite uncertainty.
This dispute may catalyze broader reforms shaping how Apple App Store policies govern AI app competition going forward. For developers and regulators alike, balancing innovation incentives with fair market access will be paramount as mobile AI applications continue their rapid growth trajectories.
By fostering transparency and accountability around App Store rankings, stakeholders can ensure a healthier competitive environment benefiting consumers worldwide.
References throughout this article include official statements from Apple's newsroom, regulatory insights from the European Commission, academic analyses via ScienceDirect, market data from Statista alongside major news coverage from CNBC and BBC.

