Google Translate Unveils AI-Powered Practice Mode to Rival Duolingo
- Ethan Carter

- Aug 28, 2025
- 15 min read

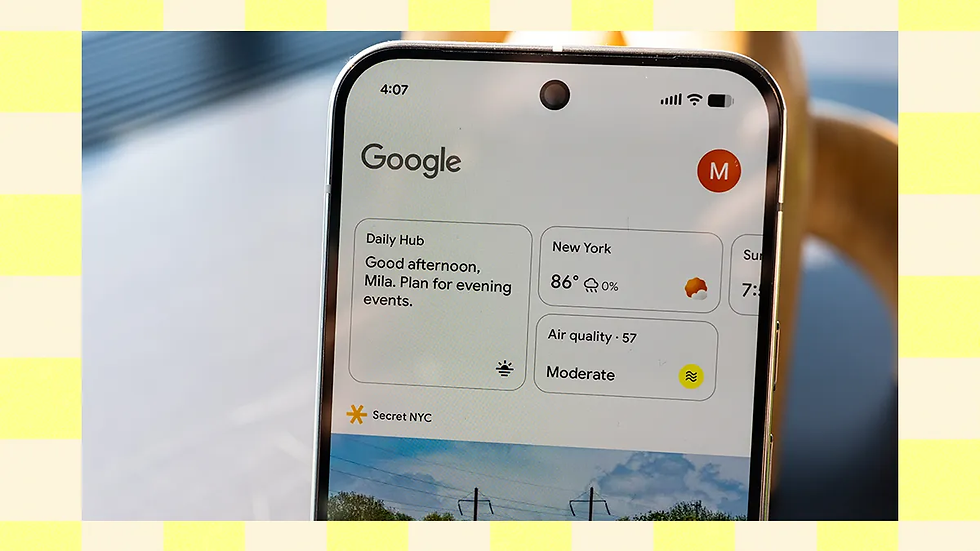
Google Translate Practice Mode is a new in-app learning feature that turns a familiar utility into an interactive learning environment. Announced by Google as an extension of Translate’s capabilities, the AI-powered Practice Mode blends short exercises, speaking and listening prompts, and integration with Live Translate to create on-the-spot language practice for existing Translate users. This matters because it lowers the barrier to entry for millions who already use Translate daily and signals a strategic push by Google to compete with Duolingo in the attention economy for language learners.
Google’s blog post introducing Practice Mode describes the feature set and rollout plans, noting integration with Live Translate and interactive practice tools that sit inside the Translate app. Early reporting indicated how Google could turn a one-off utility into a retention-focused product that keeps users practicing rather than just translating words on demand, a move that industry watchers say aims to compete with Duolingo by converting passive users into active learners.
Why this matters now: integrating bite-sized practice into an app people already have changes the adoption calculus. Instead of downloading a separate learning app, users can try short sessions where context — a street sign, an overheard phrase, or a camera scan — becomes the exercise. For learners who value convenience and immediacy, the difference between installing a new app and tapping a feature in an existing one can decide whether they practice at all.
Insight: embedding micro-lessons in a utility app leverages daily context to convert friction into habit.
Scenario: if you’re hesitant to add another subscription app to your phone, trying Practice Mode inside an app you already trust could be the low-friction way to see if short, AI-guided sessions fit your routine.
Key takeaway: Google Translate Practice Mode aims to make short, context-rich language practice ubiquitous by meeting users where they already translate, potentially reshaping who chooses a language app and why.
Google Translate Practice Mode: What the announcement says

Google framed Practice Mode as a learning layer inside Translate that offers interactive practice exercises and tight integration with Live Translate to bridge translation and active learning. The official launch language highlights in-app practice prompts, speaking and listening exercises, and use of Translate’s existing modalities (voice, camera, conversation) to create realistic practice tasks. Google’s announcement details the feature and the initial countries and languages included in the rollout, emphasizing practicality and immediate use cases like travel and daily conversation practice.
Early media coverage fleshed out the expected rollout pattern and initial language support reported for Practice Mode, suggesting a staged release on mobile platforms with the most popular languages first. Android Central’s reporting pointed to a mobile-first experience and described how Practice Mode could be surfaced inside the Translate UI, leveraging Translate’s existing user base to accelerate adoption.
If you’re deciding whether to try it now:
Try a quick session if Translate is already on your phone; you may gain immediate practice without installing another app.
Expect language coverage to expand; if your target language isn’t included at launch, watch for regional rollouts.
Use it for conversational rehearsal or quick drills, but combine with structured study for deeper grammar or literacy goals.
Actionable takeaway: Open your Translate app and look for the Practice Mode prompt; a five-minute trial will show whether the format and corrections match your learning needs.
Google Translate AI-powered Practice Mode features

Google Translate AI-powered Practice Mode features center on quick, contextual exercises that use the app’s existing inputs — voice, camera, and typed text — and layer AI-generated prompts and feedback on top. The objective is to convert translation moments into micro-learning opportunities with interactive tasks like short speaking prompts, listening comprehension, fill-in-the-blank sentence practice, and scenario-based role plays that use real-world content captured by Translate.
Types of Practice Mode exercises include:
Speaking prompts and instant pronunciation feedback based on voice inputs.
Listening tasks using short, native-like utterances to test comprehension.
Visual-context exercises that turn camera translations into practice sentences.
Short practice tests and quizzes with immediate AI-generated feedback and suggested corrections.
Forbes’s analysis highlights how Google is positioning this feature as a learning tool within Translate rather than a standalone app, noting the pedagogical potential of using real-world translation contexts as practice material. TechCrunch’s coverage explains how Practice Mode ties into Live Translate and other Translate functions to reduce friction for users who want to practice on the go.
Insight: converting everyday translations into practice items creates naturally contextualized learning, which can boost immediate retention for conversational skills.
Example scenario: you point Translate’s camera at a café menu, and Practice Mode generates a two-minute drill: translate the dish name, say a short ordering phrase aloud, and listen to a native-model audio sample — all with instant feedback.
Key UX components:
Short session flow (1–5 minutes) optimized for mobile-first use.
Clear corrective feedback: suggested rephrasing, pronunciation hints, and translation alternatives.
Light progress tracking (scores, streak-like encouragement) to nudge repeat sessions.
Actionable takeaway: Use Practice Mode for micro-practice moments (commutes, coffee breaks) and pair it with targeted review (notes or flashcards) to reinforce gains.
Core features and user flow
A typical Practice Mode session begins with a prompt (e.g., “Practice ordering coffee”), followed by a series of micro-exercises: listen to a model utterance, repeat or choose the correct reply, and receive AI-generated feedback on accuracy and phrasing. The flow emphasizes speed and clarity: prompt → response → feedback → short reinforcement item.
Because Translate is already optimized for voice and camera inputs, Practice Mode reuses those modalities to accelerate participation. Mobile-first decisions include large tap targets, concise on-screen corrections, and quick replay of native audio samples to support rapid repetition.
Scenario: a first-time user opens Practice Mode, chooses “Travel Spanish,” completes a five-minute session that includes listening and speaking tasks, and exits with a small score and a suggested two-minute follow-up exercise the next day.
Actionable takeaway: Expect Practice Mode to prioritize quick wins and repeatability over hour-long lessons, so schedule multiple short sessions rather than one long study block.
Personalization and interactivity powered by AI
Practice Mode uses adaptive difficulty — the system increases or decreases item challenge based on user responses — and pulls translation history to create personalized prompts (for example, turning recent camera translations into practice sentences). This kind of adaptive system enables targeted practice and can approximate spaced repetition by flagging weak items for future reinforcement.
AI personalization features may include:
Customized prompts derived from user activity (recent phrases, common translation errors).
Difficulty ramps that adjust vocabulary and grammar complexity automatically.
Suggested drills for identified weak points (e.g., gender agreement in Romance languages).
Scenario: an intermediate learner who frequently mistranslates subjunctive forms receives targeted sentence rewrites and short drills focusing on those constructions over several sessions.
Actionable takeaway: Use the history-driven personalization by deliberately practicing phrases you recently translated; the system can turn those moments into repeated retrieval practice.
How Practice Mode compares to typical language app features
Checklist comparison:
Gamification: lighter than Duolingo’s deep gamified ecosystem; likely to include badges or short streak nudges rather than complex leagues.
Lesson sequencing: less linear and curricular; Practice Mode favors context-driven, on-demand micro-lessons instead of a fixed syllabus.
Feedback: immediate, AI-driven corrections with examples; may lack human nuance that paid tutors or curated courses provide.
Integration: unique edge — seamless access to camera and conversation translations for real-world context.
Scenario: choosing between Duolingo and Translate: pick Duolingo for structured progression and habit loop gamification; choose Practice Mode for context-sensitive, quick practice tied to real-life translation needs.
Actionable takeaway: Treat Practice Mode as a complement to a structured course rather than a full replacement if your goal is comprehensive fluency.
AI technology powering Google Translate Practice Mode

The AI-powered Practice Mode technology rests on transformer-based architectures and multilingual translation stacks that Google has refined over years. To support interactive exercises and real-time feedback, models are fine-tuned for dialogue, pronunciation scoring, and short-form assessment tasks.
Transformer-based approaches (the dominant architecture in modern NLP) underlie current translation and generation systems and are commonly adapted for multilingual tasks and fine-tuning for conversational outputs. Research shows that careful fine-tuning and task-specific training yield better performance on pedagogical tasks like generating distractors for multiple-choice items or scoring pronunciation samples.
Insight: fine-tuning translation and generative models for assessment tasks improves engagement and feedback precision but requires task-specific data and evaluation.
Examples of model considerations:
Multilingual transformer models that share parameters across languages for transfer learning.
Fine-tuning on dialogue and question–answering datasets to create realistic prompts and responses.
Pronunciation scoring models that compare acoustic features to native norms and return graded feedback.
Actionable takeaway: product teams should measure both generation quality and pedagogical alignment when using these models — not just raw translation scores.
Underlying model architectures and training approaches
At a high level, Practice Mode likely builds on large transformer encoder–decoder or decoder-only models that support multilingual translation and generation. Fine-tuning strategies for pedagogy include supervised learning on labeled conversational datasets, reinforcement-learning-from-human-feedback (RLHF) to align outputs with helpfulness, and curricula that prioritize clarity for learners.
Multilingual transfer learning — leveraging high-resource languages to improve low-resource outputs — is a common approach that can speed expansion to more languages, but it demands careful validation to avoid introducing unnatural constructions.
Scenario (engineering): a technical PM evaluating the stack should look for models that separate translation quality (literal fidelity) from pedagogical clarity (naturalness and teachability) and ensure separate metrics for each.
Actionable takeaway: include task-specific validation datasets (native speaker ratings, educational relevance scores) in model evaluation pipelines.
How translation accuracy supports learning outcomes
High-quality translations are crucial because learners rely on feedback to correct errors and internalize patterns. If the translation or generated prompt is inaccurate or unnatural, learners can adopt incorrect phrases. Thus, translation models used in Practice Mode must balance fidelity and pedagogical clarity: sometimes a literal translation is less useful than a natural, conversational phrasing.
Research comparing machine translation outputs to human references highlights that automatic metrics (e.g., BLEU) capture some fidelity but not pedagogical suitability. Practice Mode must therefore incorporate human-centered evaluation to ensure that feedback supports learning.
Scenario: a language teacher assessing Practice Mode might test a set of prompts to check for idiomatic phrasing and to ensure generated corrections align with classroom standards.
Actionable takeaway: include human-in-the-loop checks in the early rollout to catch frequent unnatural phrasing and refine generation templates.
Continuous improvement and real-time inference constraints
Delivering instant feedback involves trade-offs between latency and model complexity. On-device inference reduces latency and supports privacy but is constrained by model size; cloud inference enables larger models but adds network dependency. Google will likely combine both: smaller on-device models for latency-sensitive scoring and cloud-backed models for richer, personalized content.
Privacy and opt-in models are central: Practice Mode should surface clear options for users to exclude their practice data from training and to understand how corrections might be used to improve models.
Scenario (product): when deciding whether to roll out regionally constrained features, weigh local latency and data privacy regulations that might require on-device-only solutions.
Actionable takeaway: design hybrid inference strategies and transparent privacy settings to balance accuracy, responsiveness, and trust.
How Google Translate Practice Mode competes with Duolingo and market implications

Google Translate’s move into active learning represents a strategic extension of a utility into an engagement product. With an existing global user base, tight integration across Google services, and a reputation for translation quality, Translate can disrupt typical distribution and retention models used by standalone apps like Duolingo.
Analysts have framed this shift as Translate evolving from a utility to an engagement platform, which changes metrics companies prioritize, such as session length and repeat visits rather than outright downloads. Financial commentary has flagged this entry as material to market dynamics — incumbents will need to adapt to a major platform play that can redirect casual learners and travel users into free micro-practice inside an existing ecosystem.
Insight: distribution beats curriculum early — Google’s scale means attention capture is the immediate battleground, while pedagogical depth is a longer-term competition.
Example: a traveler who previously used Translate for quick phrases may now practice short role-play sessions right before a trip, reducing the need to download a separate learning app for the same immediate benefit.
Actionable takeaway: incumbents should focus on deep pedagogical value and differentiated community or certification features to defend monetized segments.
Competitive strengths and go-to-market advantages
Google’s advantages:
Massive distribution through Android, Chrome, and default app placements.
Cross-product synergies (Search, Maps, Assistant) to surface contextual practice prompts.
Built-in trust and familiarity for millions of users.
Potential monetization paths include optional premium features (deeper progress tracking, offline advanced models), ad-supported free tiers, or enterprise/education partnerships that integrate Practice Mode into classroom tools.
Scenario: a Duolingo product team might prioritize retention and depth by enhancing tutoring options or certified assessments to differentiate from Google’s micro-practice approach.
Actionable takeaway: monitor engagement funnels (convert Translate users into repeat practice users) to evaluate real threat levels to incumbents.
Market size and adoption signals to monitor
Key KPIs investors and product teams should watch:
Adoption rate of Practice Mode among existing Translate users.
Session length and frequency (are users returning for micro-lessons?).
Retention curves and conversion to any premium offerings.
Cross-product lift (e.g., are Maps or Search queries linking to Practice Mode content?).
Early signals may come from regional rollouts and how quickly active Translate users try practice sessions versus only using basic translation. Analysts will watch public usage stats and any shifts in Duolingo’s engagement metrics as potential indicators.
Scenario (investor brief): track week-over-week active users for Practice Mode and compare retention against baseline Translate usage and Duolingo’s daily active user trends.
Actionable takeaway: set up benchmarks for micro-session uptake (e.g., percentage of daily Translate users who try Practice Mode within 30 days) to gauge product-market fit.
Strategic risks and responses from incumbents
Risks for Google:
Perception mismatch: Translate users expect utility, not a learning app; poor onboarding could reduce engagement.
Pedagogical limitations: if Practice Mode lacks curricular depth, serious learners will prefer dedicated apps.
Regulatory scrutiny: large platform moves into consumer education could attract attention in competitive markets.
Likely incumbent responses:
Duolingo and others may double down on personalization, community features, and paid certifications.
Partnerships with institutions or credentialing bodies to offer recognized progress paths.
Emphasis on learning science-backed curriculum and human tutor integrations.
Scenario (strategic recommendation): incumbents should accelerate features that are costly for a platform newcomer to replicate quickly (human tutoring, accredited certificates, curated curricula).
Actionable takeaway: incumbents must sharpen their unique value — proven pedagogy, assessment credibility, and monetizable advanced features.
Research evidence: Effectiveness of AI-driven practice and translation reliability

Academic research provides early support for AI-driven practice tests while also flagging limitations in machine-generated language characteristics. Studies suggest that AI can generate valid practice items and support automated assessment, but quality control, validation, and hybrid human oversight improve learning outcomes.
Recent empirical work shows promise for AI-generated practice tests in predicting short-term proficiency gains and supporting formative assessment when items are validated. Other studies examine machine-generated language and note tendencies toward formulaic or unnatural phrasing that may mislead learners if left unchecked.
Insight: AI can scale practice and assessment, but learning gains depend on item validity and human-centered validation.
Example: an automated practice item that mirrors classroom exercise structure (prompt, distractors, feedback) can help drill grammar points effectively if reviewed for naturalness.
Actionable takeaway: blend AI generation with curated templates and periodic human review to maintain pedagogical integrity.
Evidence supporting AI-generated practice tests
Empirical studies indicate that AI can produce effective practice items that map to learning objectives and that, when integrated into a study regimen, can predict short-term gains in targeted competencies. Automated scoring combined with corrective feedback helps learners iterate faster than waiting for human correction.
Scenario (program director): before integrating AI tests into a curriculum, pilot with a control group and measure retention and transfer to communicative tasks, not just item-level accuracy.
Actionable takeaway: implement A/B tests that measure real communicative outcomes (speaking fluency or listening comprehension) rather than only item-level correctness.
Limitations from machine-generated language characteristics
Research reveals that machine-generated outputs can be overly formulaic, occasionally unidiomatic, and sometimes biased toward training data patterns. These issues risk teaching non-native or stilted forms if AI outputs aren’t curated.
Mitigation strategies include:
Hybrid human-in-the-loop checks for edge-case items.
Curated prompt templates to constrain generation to natural phrasing.
Confidence scoring to flag low-certainty items for review.
Scenario (teacher): curate a bank of AI-generated prompts and vet them monthly to remove unnatural constructions before assigning to students.
Actionable takeaway: use confidence scores and human review to filter problematic items and reduce the risk of learners picking up unnatural phrasing.
Bridging research and product design
Design patterns that arise from the research include surfacing confidence scores, offering explainable feedback (why an answer is incorrect), and enabling easy reporting or correction suggestions from users. Longitudinal studies and randomized trials are crucial to validate learning gains beyond short-term improvements.
Scenario (product roadmap): schedule longitudinal assessments and partner with academic researchers to publish on learning efficacy as the product scales.
Actionable takeaway: allocate product and research resources to multi-week studies that tie Practice Mode activity to communicative proficiency improvements.
Practice Mode adoption challenges, accuracy concerns, and industry trends

Practice Mode adoption faces both behavioral and technical hurdles. Users may not immediately equate a translation tool with a learning platform; accuracy concerns and privacy questions also influence trust. Yet the feature aligns with broader AI-in-education trends toward personalization and automated assessment.
Surveys and analyses of AI’s impact in language learning outline adoption patterns and caution on quality assurance, suggesting pathways for platform entrants and incumbents. Work on AI integration trends in education shows growing appetite for personalization, but stresses the need for transparency and human oversight in high-stakes learning contexts.
Insight: bridging utility and education requires careful onboarding, trust-building, and a clear product promise.
Main adoption challenges and competitive barriers
Key challenges:
Habit inertia: users may not change behavior to practice without strong nudges.
Expectation gap: users expect utility apps to be reliable translations, not educational journeys.
Retention mechanics: Translate needs retention hooks that respect its utility identity.
Recommended solutions:
Targeted onboarding that frames Practice Mode as a low-commitment experiment.
Gamified micro-lessons that reward repeated short sessions without over-gamifying the core utility.
Partnerships with educators to validate content and endorse practice workflows.
Scenario (growth playbook): implement an optional guided tour that demonstrates a five-minute practice session and suggests a daily micro-practice routine with push reminder opt-ins.
Actionable takeaway: use incremental nudges and context-triggered prompts (e.g., after a camera translation) to convert translation moments into practice habits.
Accuracy, trust, and safety concerns
Concerns include incorrect feedback leading to fossilized errors, overconfidence from AI assessments, and bias in training data producing skewed outputs. Solutions:
Show confidence labels and alternative phrasings.
Provide easy reporting for incorrect items and fast remediation.
Offer localized human review pipelines for critical languages or educational deployments.
Scenario (risk assessment): an educational institution should require review workflows before integrating Practice Mode into graded assignments.
Actionable takeaway: require explicit opt-in for data sharing to train models and surface clear privacy settings to preserve trust.
Industry trends and where Practice Mode fits
Trends to watch in the next 12–24 months:
Convergence of utility apps and learning features as platforms pursue engagement.
Growth of hybrid models combining AI practice with human tutoring on-demand.
Emergence of certification partnerships as evidence of learning value.
Possible next steps for Practice Mode: certified progress pathways, API access for third-party educational platforms, and more robust curricular sequencing for learners who want depth.
Scenario (five-year horizon): language learning ecosystems may evolve into interconnected stacks — core platforms offering micro-practice and discovery, specialized apps delivering deep curricula, and credentialing partners validating proficiency.
Actionable takeaway: product teams should prioritize interoperability (exportable progress data, APIs) to create partnerships that extend the feature’s value.
Conclusion: Trends, opportunities, and FAQ
Google Translate Practice Mode is an important step in making language practice ubiquitous by embedding AI-driven micro-learning into a utility millions already use. Over the next 12–24 months expect continued feature expansion, improved model accuracy, and competitive responses from dedicated language apps that emphasize depth and certification.
Near-term trends (12–24 months):
Wider rollout of Practice Mode languages and regional availability.
Hybrid inference strategies to balance latency, accuracy, and privacy.
Product responses from incumbents focusing on certifications and tutoring.
Increased emphasis on transparency (confidence scores and data controls).
New partnership models linking platform-scale practice with accredited learning.
Opportunities and first steps:
For Google: roll out robust onboarding, confidence indicators, and educator partnerships to validate pedagogical claims.
For incumbents: double down on pedagogical depth, community features, and credible assessments.
For educators: pilot Practice Mode for formative assessment but require human validation before high-stakes use.
For investors: watch adoption and retention KPIs over the first 6–12 months as signals of product–market fit.
For learners: try Practice Mode for context-driven practice and combine it with structured study for grammar and literacy.
Working theory: distribution and convenience will drive initial adoption, while pedagogical rigor will determine long-term displacement of incumbents.
Actionable next steps: try a short session in Practice Mode, track whether it changes your daily practice habits, and for product teams, instrument micro-session funnels to learn what nudges drive repeat use.
FAQ
Q1: Is Practice Mode free and which languages are supported? A1: Google launched Practice Mode as an integrated feature inside the Translate app; availability and supported languages vary by rollout and region. Check Google’s official announcement for the initial language set and regional availability details in the same post that introduced the feature to users. Google’s official announcement explains the rollout and initial language coverage.
Q2: How accurate is the feedback and can I trust it for formal study? A2: The feedback leverages Google’s translation and speech models and can be reliable for conversational practice, but it may not substitute for structured courses. Use Practice Mode for speaking and listening drills and validate critical items with teachers or certified materials.
Q3: How does Practice Mode differ from Duolingo in teaching approach? A3: Practice Mode focuses on contextual, on-demand micro-practice integrated into real-world translation moments, whereas Duolingo provides a more structured, gamified curriculum and progression system. Both approaches can complement each other depending on learner goals.
Q4: Will my practice data be used to train Google’s models? A4: Data policies vary; Google typically provides opt-in/out controls and aggregates data for model improvement when permitted. Review Translate’s privacy settings and the feature’s in-app notices for explicit information about data use and opt-out choices.
Q5: Can educators use Practice Mode to assess students? A5: Practice Mode is useful for formative tasks and low-stakes practice, but educators should be cautious about high-stakes assessment without human validation due to possible generation quirks and accuracy limitations.
Q6: What metrics will show whether Practice Mode is succeeding? A6: Key indicators include adoption rate among Translate users, frequency of micro-sessions, retention over 7–30 days, cross-product lift, and, for validated learning outcomes, improvements on external communicative assessments.
For broader commentary on implications for adoption and industry strategy, expert discussions in technology podcasts offer context on platform moves and product strategy and on corporate product evolution in Google’s ecosystem. This Week in Google also provides perspective on how platform plays can shift product expectations across user bases.
Final practical tip: if you already use Google Translate regularly, enable Practice Mode and try a 3–5 minute session before your next trip or conversation practice — it’s the quickest way to see how the AI-powered Practice Mode fits into your learning routine and whether it can replace or complement the apps you already use.