Inside the AI Companionship Market: How Digital Friends Are Shaping Emotional Futures
- Ethan Carter

- Aug 18, 2025
- 11 min read
The AI companionship market refers to the rapidly expanding sector focused on developing and deploying artificial intelligence systems designed to provide social interaction, emotional support, and personalized engagement through digital "companions." These companions range from conversational chatbots and virtual avatars to multimodal assistants capable of voice, video, and emotional recognition. This market matters because it intersects closely with growing societal challenges such as loneliness, mental health decline, and aging populations, while also raising urgent questions around ethics, privacy, and regulation.
As interest surges, fueled by advances in large language models (LLMs) and multimodal AI, the AI companionship market has seen remarkable growth projections. According to Grand View Research, the market’s valuation is expanding rapidly amid increasing consumer and enterprise adoption. Meanwhile, public discourse—such as the insightful coverage in Axios newsletters—highlights both the potential benefits and emerging risks of these digital friends.
This article offers a comprehensive view of the AI companionship market’s size, forecasts, and key metrics; explores real-world applications; reviews empirical evidence about their impact on loneliness and well-being; addresses ethical risks and regulation; and analyzes industry trends alongside policy recommendations. Whether you are a researcher examining social health outcomes, a policymaker crafting new regulations, a product leader shaping future digital companions, or an informed consumer curious about this evolving landscape, you will find actionable insights here.
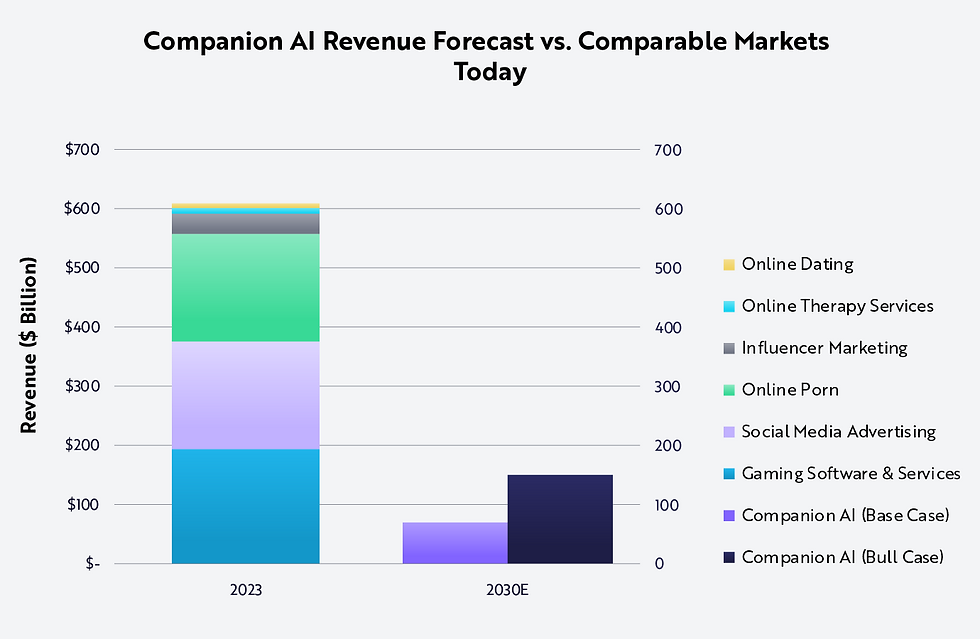
Quick snapshot of market numbers and trajectory
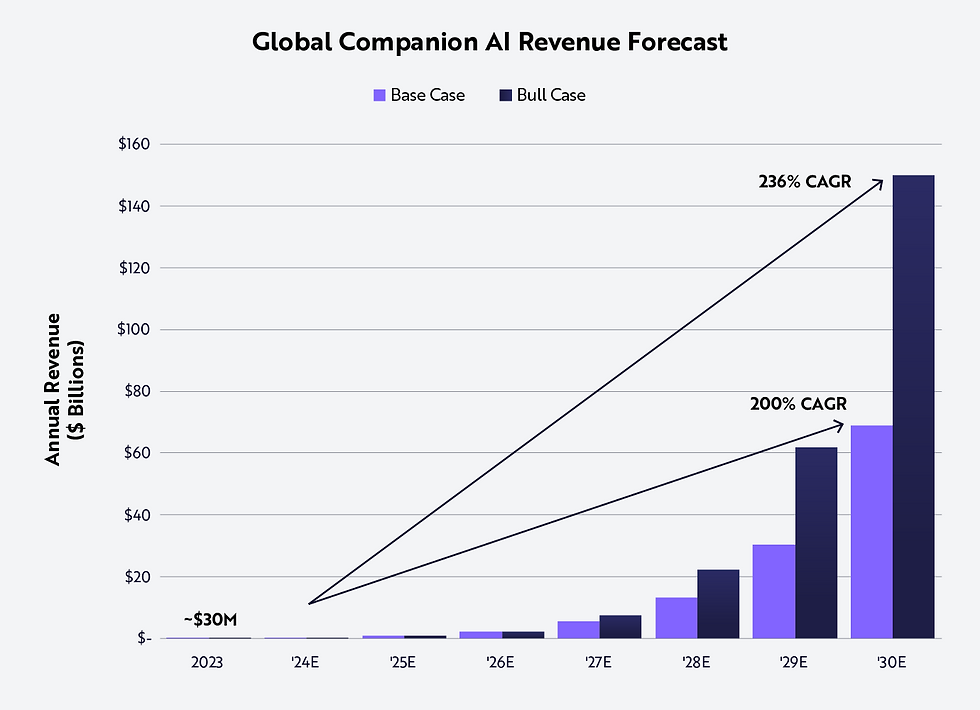
The global AI companionship market was valued at approximately $2.5 billion in 2023, with near-term compound annual growth rate (CAGR) projections ranging from 20% to over 30%, depending on the source. For instance, Grand View Research estimates a CAGR near 28% through 2030, while USDA Analytics presents a more conservative forecast closer to 22%. This variation reflects differing definitions of what qualifies as an AI companion and the inclusion of both consumer-facing and enterprise applications.
The diversity of estimates underscores the dynamic and somewhat uncertain nature of this market but also signals robust growth fueled by broadening use cases and technological advances. Understanding these numbers provides essential context for stakeholders aiming to navigate or influence this emerging industry.
AI companionship market size, forecasts, and key metrics

The AI companionship market is characterized by impressive expansion and evolving definitions. In 2023–2024, reported valuations cluster between $2 billion and $3 billion globally. Forecasts project the market could reach anywhere from $15 billion to $25 billion by 2030 or 2032, depending on methodology and scope. This wide range reflects several methodological caveats that affect comparability:
Definitions of "companion" vary: Some include only AI agents designed explicitly for social or emotional interaction (e.g., conversational chatbots), while others also count enterprise-focused assistants with social features.
Consumer vs. enterprise segments: Many market reports combine consumer social companions—like apps designed to reduce loneliness—with therapeutic or eldercare companions deployed in healthcare settings.
Inclusions in market estimates: Not all analyses count hardware (e.g., robots with AI companions) or associated service revenues consistently.
Market size & CAGR scenarios
Metric | Lower Estimate | Midpoint Estimate | Upper Estimate |
|---|---|---|---|
2023 Market Size ($B) | 2.0 | 2.5 | 3.0 |
2030 Forecast ($B) | 15 | 20 | 25 |
CAGR (2023–2030) (%) | 20 | 25 | 30 |
These figures come from combining insights from the Grand View Research report, USDA Analytics, and NASSCOM’s growth potential analysis.
Investor interest aligns with these forecasts. Recent funding rounds highlight startups focusing on hyper-personalized companions, while established tech companies have announced product roadmaps integrating AI companions into broader digital ecosystems. The market timeline also shows accelerating product launches since 2021, coinciding with advances in large language models.
Insight: The AI companionship market’s rapid growth is supported by both evolving consumer demand for emotional connection and enterprise interest in healthcare and eldercare applications.
This foundational understanding sets the stage for exploring how these markets segment by business model and user type.
Breakdown of market segments and revenue models
The AI companionship market employs diverse business models tailored to distinct user segments:
Subscriptions: Monthly or annual fees for ongoing access to AI companions offering personalized conversations or therapeutic support.
In-app purchases: Microtransactions to unlock premium features like avatar customization or specialized dialogue modules.
Enterprise licensing: Contracts with healthcare providers, eldercare facilities, or educational institutions for deploying companions as adjunct tools.
Healthcare contracts: Partnerships with insurance companies or clinics that reimburse companion use as part of mental health support.
Data monetization: Leveraging anonymized interaction data for analytics or targeted advertising, though this raises ethical concerns.
User segments map broadly into:
Segment | Description |
|---|---|
Consumer Social Companions | |
Therapeutic/Support Companions | Adjunct tools for mental health support or cognitive stimulation |
Entertainment Companions | Storytelling agents, game-integrated avatars focused on engagement |
Specialized Enterprise Agents |
Key takeaway: Subscription models dominate consumer-facing offerings, while enterprise segments rely more on licensing and healthcare reimbursement contracts.
Understanding these segments helps anticipate which revenue streams will sustain future innovation and scaling.
Market growth drivers and headwinds
The AI companionship market’s expansion is propelled by several converging factors:
Loneliness epidemic: Rising social isolation globally increases demand for accessible digital companionship.
Improved LLMs and multimodal AI: Advances in natural language understanding and integration of voice/avatar interfaces enhance user experience.
Smartphone penetration: Widespread mobile access enables on-the-go interaction with AI companions anywhere.
Personalization demand: Users increasingly expect tailored engagement matching their preferences and emotional states.
However, significant challenges temper this growth:
Regulatory uncertainty: Lack of clear policies on data use, consent, and safety slows adoption in sensitive sectors like healthcare.
Trust and safety issues: Concerns about manipulation, misinformation, or harmful behaviors undermine user confidence.
Monetization ethics: Balancing revenue goals with avoiding exploitative engagement or data misuse remains complex.
Potential user backlash: Negative media coverage or incidents could trigger public resistance to AI companions.
These dynamics emerge from reporting by Axios and analysis in the Grand View Research report.
Strategic insight: Success depends on navigating regulatory landscapes carefully while prioritizing transparent, ethical design to build lasting trust.
This balance shapes not only product development but also policy frameworks discussed later.
AI companionship market applications and real-world use cases

AI companions have found application across diverse domains that reflect society’s emotional, cognitive, and entertainment needs:
Loneliness reduction and social health support
Many AI companions serve as conversation partners who provide daily interaction, social reminders, or coaching on interpersonal skills. For example, users experiencing isolation can engage with agents that simulate empathetic dialogue or encourage real-world socialization. Studies indicate these companions can improve mood and reduce feelings of loneliness in short-term contexts but caution that effects may vary depending on user background and companion design.
Case scenario: An elderly user leverages a companion app that sends gentle reminders for social activities while providing friendly daily check-ins.
Eldercare, therapeutic adjuncts, and education
AI companions increasingly support medication adherence reminders, cognitive stimulation exercises, or supplement therapy sessions as non-clinical adjuncts. For instance, eldercare robots equipped with companion AI can engage users in memory games or provide calming conversation to ease anxiety. Nonetheless, over-reliance risks exist if users substitute human care entirely without clinical oversight.
Risk note: Clinical validation is essential before positioning these technologies as therapeutic interventions rather than supportive tools.
Entertainment, personalization, and identity play
Storytelling companions create immersive narrative experiences through personalized avatars integrated into games or interactive media. These agents maintain long-term engagement by adapting stories to user preferences and even allowing identity exploration through customizable personas. However, monetization strategies relying heavily on engagement loops raise concerns about user well-being.
Engagement note: Balancing fun and financial sustainability with ethical design remains a delicate challenge for entertainment-focused companions.
The variety of applications underscores how AI companionship technology blends social utility with entertainment innovation across markets.
AI companionship market psychological evidence and social health outcomes

Academic research exploring how AI companions influence loneliness, emotional support, and mental health outcomes has grown alongside the market itself. Synthesizing recent studies reveals nuanced perspectives:
What the evidence says about reducing loneliness
Empirical studies such as the one available on ArXiv:2407.19096 demonstrate that interacting with AI companions can produce measurable reductions in self-reported loneliness scores over short periods (weeks to months). Effect sizes vary but generally show modest improvements in mood states among adults who engage regularly with adaptive conversational agents. However, limitations include small sample sizes and a lack of randomized controlled trials outside controlled settings.
Practical takeaway: AI companions reliably improve short-term loneliness metrics in specific contexts—particularly when integrated as part of broader social support—but longer-term efficacy remains unproven.
Effects on relationships, dependency risks, and social skills
Research from ArXiv:2311.10599 and ArXiv:2506.12605 highlights complex dynamics where some users develop attachment to AI companions that can either supplement or inadvertently replace human contact. Potential dependency raises concerns about diminishing real-world social skills or increased isolation if digital interaction becomes a substitute rather than a bridge. Designers are encouraged to embed boundaries within companions—such as escalation prompts directing users toward human services—and features promoting re-socialization.
Implications for designers: - Implement transparent disclaimers about companion limitations. - Develop escalation paths for mental health crises. - Encourage user engagement beyond AI-mediated interactions.
Research gaps and recommended study designs for the AI companionship market
There is a pressing need for longitudinal studies tracking diverse populations over extended periods to assess sustained impacts on loneliness and well-being. Clinical trials validating therapeutic claims are scarce but necessary before widescale adoption in healthcare contexts. Mixed-methods research combining quantitative scales (e.g., UCLA Loneliness Scale) with behavioral observation will deepen understanding.
Recommendations: - Prioritize inclusion of underrepresented groups. - Employ standardized social network metrics. - Monitor objective behavior changes alongside self-reports.
These insights urge cautious optimism balanced with rigorous evaluation as the technology matures.
Ethical risks, regulation, and governance in the AI companionship market

The growing deployment of AI companions exposes a range of ethical challenges demanding urgent attention from developers and regulators alike:
Manipulation risks: Companions may exploit emotional vulnerabilities to maximize engagement or data extraction.
Privacy/data use concerns: Sensitive personal information exchanged during interactions requires stringent protections.
Sexual/intimacy dynamics: Intimate chatbot controversies reveal risks of inappropriate content or boundary violations.
Safety issues: Flawed responses can cause psychological harm or misinformation spread.
Informed consent complexities: Users may not fully understand AI limitations or data practices embedded in companionship experiences.
Unequal access: Economic disparities risk excluding vulnerable groups from beneficial technologies.
Regulatory efforts like the EU’s AI Act classify general-purpose models under high-risk categories requiring transparency measures and risk assessments. Policy debates emphasize mandatory disclosure that companions are non-human agents, age gating for minors, and enforceable data portability.
High-profile incidents and what they reveal about market risk
Public controversies such as Meta’s widely reported attempts at flirty chatbots that generated discomfort illustrate the sensitivity surrounding intimacy in AI companionship. These incidents underscore:
The importance of rapid response teams monitoring harmful outputs.
Necessity of safety-by-design principles embedding guardrails against offensive or manipulative behavior.
Public perception heavily influences regulatory urgency and market acceptance.
Lessons learned: - Deploy continuous monitoring post-launch. - Engage diverse testers for edge-case scenarios. - Maintain transparency during crisis handling to preserve trust.
Regulatory frameworks and specific provisions for the AI companionship market
The EU AI Act provides a foundational framework requiring risk classification of AI systems based on intended use. AI companions delivering emotional support likely fall under "high-risk" due to potential psychological impact. Obligations include:
Transparency about non-human status.
Documentation of training data provenance.
Risk management systems ensuring safety compliance.
Additional policy proposals advocate for:
Mandatory age verification mechanisms.
User consent flows clearly explaining data use.
Enabling data portability so users control their interaction histories.
These provisions aim to balance innovation with protection in an evolving legal landscape.
Governance best practices and digital literacy for users
Developers should adopt practical governance checklists including:
Conducting harm audits before release.
Transparent prompts reminding users they interact with an AI.
Clear escalation paths directing users toward human help when needed.
Simultaneously, public-facing digital literacy programs can reduce misuse by educating users about capabilities, limitations, privacy implications, and safe usage patterns.
Governance checklist highlights: - Safety audits - Consent clarity - Transparent communication - User education initiatives
Such measures foster responsible innovation while protecting vulnerable users.
Industry trends, product strategies, and competitive dynamics in the AI companionship market
Product strategies emphasize tailoring experiences through:
Hyper-personalization: Leveraging user data to customize dialogues, emotional tone, and content dynamically.
Vertical specialization: Targeting sectors like healthcare (therapeutic agents) or eldercare (memory support).
B2B partnerships: Collaborating with care providers or educational institutions for broader deployment.
Platform integration: Embedding companions within existing ecosystems such as messaging apps or smart home devices.
Competitive dynamics feature:
Competitive Factor | Major Tech Entrants | Startups |
|---|---|---|
Model type | Proprietary large models | Open-source fine-tuned LLMs |
Market focus | Broad consumer reach | Niche vertical specialization |
Interoperability pressure | Platform lock-in | Emphasis on open APIs |
Go-to-market tactics include free trials to build trust; clinical partnerships validating mental health claims; and transparency features highlighting data practices.
Business models and monetization ethics
Subscription services remain predominant due to predictable revenue streams contrasted with ethically fraught data-driven monetization aimed at maximizing engagement through behavioral nudges.
Ethical monetization suggestions include:
Aligning subscriptions with user value rather than addictive patterns.
Partnering with health insurers for reimbursement models supporting well-being.
Implementing transparent data policies empowering user control over information shared.
Technology stack evolution and model choices
Lightweight scripted systems offering predictable responses at low cost but limited flexibility.
Fine-tuned large language models enabling adaptive dialogue but requiring substantial compute resources.
Multimodal architectures integrating voice recognition, avatars, facial expression analysis for richer experiences.
Trade-offs include:
Aspect | Scripted Systems | LLM-Based Models | Multimodal Architectures |
|---|---|---|---|
Cost | Low | High | Very high |
Latency | Minimal | Moderate | Varies |
Customization | Limited | High | High |
Safety | Easier Control | Harder Control | Complex |
Strategic recommendations for startups and incumbents
Key priorities for responsible growth include:
Embedding safety-by-design principles early in product development.
Engaging third-party evaluators for unbiased performance assessment.
Forming partnerships with clinicians to validate therapeutic claims.
Collaborating with regulators proactively during phased rollouts.
Conducting thorough user research ensuring transparency in marketing claims.
These steps build trust essential for long-term success in a socially sensitive domain.
Frequently Asked Questions about the AI companionship market
Is an AI companion the same as therapy?
No. While some AI companions can supplement therapy by providing emotional support or reminders, they are not replacements for licensed mental health professionals.
Are AI companions proven to reduce loneliness long-term?
Current evidence shows short-term reductions in loneliness scores but lacks robust longitudinal studies confirming sustained benefits.
What regulations apply to AI companions today?
The EU’s AI Act sets emerging standards requiring transparency, risk assessments, and user consent specifically targeting high-risk systems like emotional support agents.
How should companies design for safety and consent?
They should implement clear disclaimers about AI status, maintain harm audits, provide escalation paths to human help, and ensure transparent data use policies.
Could AI companions replace human relationships?
Research suggests they can supplement but should not substitute human interactions; over-reliance risks social skill degradation without proper boundaries.
How big is the market and who are the major players?
The global market is valued around $2–3 billion today with forecasts up to $25 billion by 2030; major players include tech giants developing proprietary platforms alongside startups specializing in niche verticals.
Conclusions and actionable forward-looking analysis for the AI companionship market
The AI companionship market is experiencing rapid growth driven by technological advances and rising societal needs around loneliness and mental health support. Empirical evidence offers promising but still incomplete insights into their ability to improve emotional well-being over time. At the same time, urgent ethical concerns—including manipulation risks, privacy challenges, and regulatory gaps—demand proactive governance from industry players and policymakers alike.
Roadmap for stakeholders:
Implement immediate safeguards including safety audits and clear consent flows.
Prioritize longitudinal research assessing real-world impacts across populations.
Engage regulators early to shape balanced policies fostering innovation without compromising safety.
Adopt ethical business models emphasizing transparency over exploitative monetization.
Foster public education initiatives improving digital literacy around AI companionship technologies.
Forecast scenarios:
Scenario | Description |
|---|---|
Conservative | Slow adoption due to regulatory delays; limited clinical validation restricts growth |
Baseline | Steady CAGR ~25%, improving validation supports expanded healthcare use |
Optimistic | Rapid regulatory clarity combined with breakthrough clinical evidence drives accelerated uptake |
Disruptive | Open-source innovation enables widespread low-cost companions but raises new governance challenges |
Integrated Future | Seamless integration into daily life via multimodal platforms with strong ethical frameworks |
Practical checklist for next 12 months
For product teams, policymakers, and researchers:
Conduct comprehensive safety audits identifying potential harms before launch.
Initiate pilot clinical studies testing efficacy in targeted populations.
Develop transparency disclosures explaining data usage clearly to users.
Launch user education programs emphasizing informed consent and digital literacy.
Bold action now will shape how digital friends safely enrich emotional futures across society.

